
Worried about your horse’s health? Learn about the most common horse health problems in 2024, including colic, ulcers, Potomac Horse Fever, and more. Discover solutions & prevention tips to keep your equine friend happy & thriving! #horsehealth #equinecare
Keeping Your Horse Healthy: Most Common Horse Health Issues and Solutions in 2024
Horses are majestic creatures that bring joy and companionship to many. But like all living beings, they are susceptible to various health problems. Early detection and proper treatment are crucial for ensuring your horse’s well-being. This comprehensive guide explores the most common horse health issues in 2024 and provides solutions to keep your equine friend happy and healthy.
Most Common Horse Health Issues and Solutions
Colic
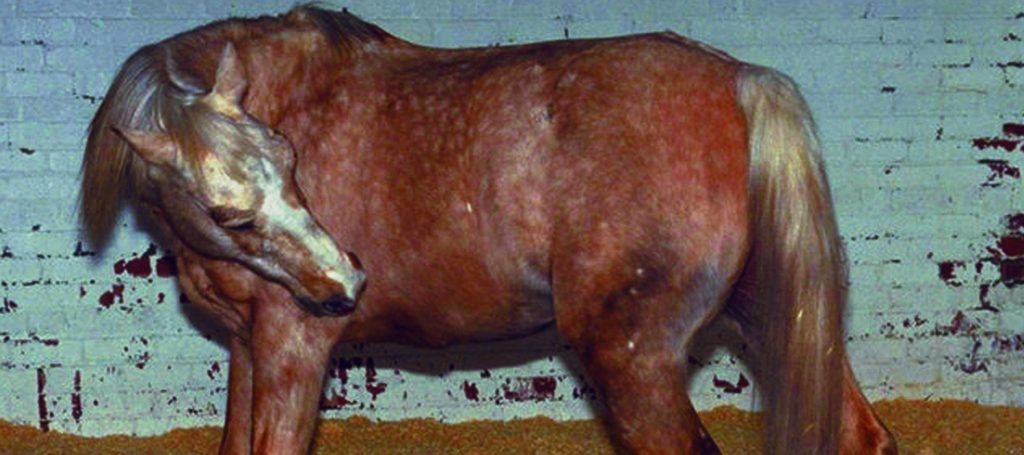
Colic is a general term for abdominal pain in horses. It can be caused by various factors, including:
- Impaction (digestive material gets stuck)
- Gas colic (excessive gas buildup)
- Displacement (organs move out of position)
- Strangulation (twisting or entrapment of intestines)
Symptoms:
- Pawing at the ground
- Rolling
- Flank pain
- Lack of appetite
- Lethargy
Solutions:
- Prevention: Regular feeding schedules, high-quality hay, and ensuring adequate water intake are key to preventing impaction colic.
- Early Detection: Monitor your horse’s behavior for any signs of colic. Early diagnosis can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment.
- Veterinary Care: If you suspect colic, contact your veterinarian immediately. Depending on the severity, treatment may involve pain medication, fluids, or even surgery.
Gastric Ulcers
Gastric ulcers are sores that develop on the lining of the horse’s stomach. They are often caused by:
- Stress
- NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) use
- Heavy grain meals
- Lack of forage
Symptoms:
- Weight loss
- Poor appetite
- Depression
- Flehmen response (curling upper lip)
- Colic-like symptoms
Solutions:
- Diet Management: Feeding a high-fiber diet with smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent ulcers. Consider adding a buffer like soaked beet pulp to their diet.
- Stress Reduction: Minimize stress factors in your horse’s environment. This may involve providing turnout time with other horses, creating a calm atmosphere, and avoiding harsh training methods.
- Veterinary Treatment: Veterinarians can prescribe medications to help heal ulcers and reduce stomach acid production.
Nutritional Support for Gastric Health
Several commercially available horse feeds are formulated to promote gut health and prevent ulcers. These feeds often contain high levels of fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics, which can help create a healthy gut environment.
Potomac Horse Fever (PHF)

Potomac Horse Fever (PHF) is a mosquito-borne viral disease that primarily affects horses in the eastern and southeastern United States.
Symptoms:
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Depression
- Muscle weakness
- Facial swelling
- Difficulty swallowing
- Abortion in pregnant mares
Solutions:
- Vaccination: Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent PHF. Consult your veterinarian to determine the appropriate vaccination schedule for your horse.
- Mosquito Control: Minimize mosquito breeding grounds around your horse’s environment by eliminating standing water sources.
Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS)

Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS) is a hormonal disorder similar to type 2 diabetes in humans. It is becoming increasingly common with the rise of obesity in horses.
Risk Factors:
- Obesity
- Insulin resistance
- Lack of exercise
Symptoms:
- Lethargy
- Difficulty shedding winter coat
- Recurrent infections
- Laminitis (inflammation of the hooves)
Solutions:
- Weight Management: A veterinarian can help create a weight management plan for your horse, which may include dietary changes and increased exercise.
- Exercise: Regular exercise is crucial for managing EMS. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD)
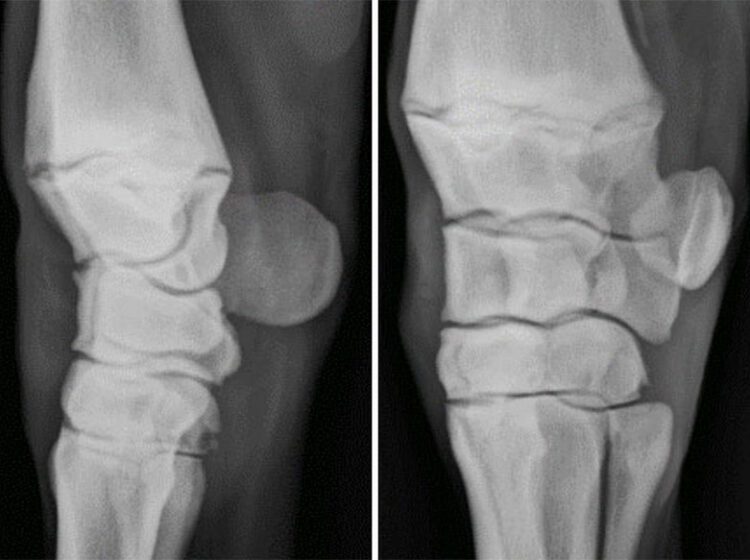
Degenerative Joint Disease (DJD), also known as osteoarthritis, is the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. It is a common condition in older horses and can be caused by:
- Age
- Injury
- Overwork
- Conformation (the horse’s build)
Symptoms:
- Stiffness
- Lameness
- Difficulty rising or lying down
- Reluctance to move
Solutions:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the joints.
- Joint Supplements: Veterinarians may recommend joint supplements containing glucosamine, chondroitin, and hyaluronic acid to support joint health.
- Pain Management: Medications can help manage pain and improve your horse’s comfort.
- **Exercise Management

Leave a Reply